The Comprehensive Guide on How to Resize an Image
Learn the fundamentals of image resizing, including aspect ratios, resolution, and file formats, to ensure your images look perfect on any platform.
Why Resize Images?
In today's digital world, images are everywhere. From social media posts to e-commerce product listings, high-quality visuals are crucial for engagement. However, using oversized images can lead to slow page load times, poor user experience, and even lower search engine rankings. Resizing images to the optimal dimensions for their intended use is a fundamental step in web and content management.
- Faster Loading Times: Smaller file sizes mean your website or app loads quicker.
- Improved SEO: Search engines like Google favor fast-loading websites.
- Better User Experience: No one likes waiting for large images to load.
- Platform Compliance: Many platforms have specific requirements for image dimensions.
Key Concepts in Image Resizing
Before you start resizing, it's helpful to understand a few key terms:
Pixels
The smallest unit of a digital image. Dimensions are often measured in pixels (e.g., 1920x1080).
Aspect Ratio
The proportional relationship between an image's width and height (e.g., 16:9).
Resolution
The detail an image holds, often measured in DPI (dots per inch) for print or PPI (pixels per inch) for screens.
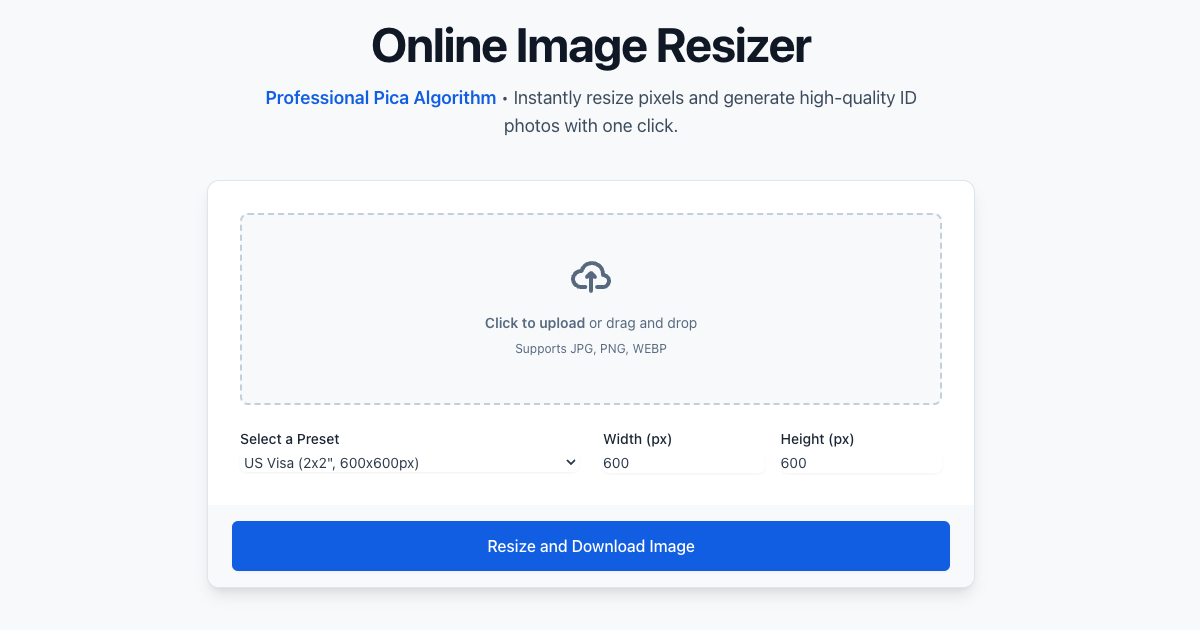
How to Use Our Online Image Resizer
Our tool makes resizing images a breeze. It's fast, free, and respects your privacy by processing everything in your browser.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
- Stretching: Don't distort your image by changing the width or height independently without maintaining the aspect ratio.
- Upscaling: Avoid making an image larger than its original size, as this can lead to pixelation and loss of quality.
- Over-compression: Saving an image at too low a quality setting can introduce artifacts and blurriness.